Recently, the remotely sensed nighttime light map of China from Luojia-1A 01 satellite is released. Free data service is available to users from all walks of life.
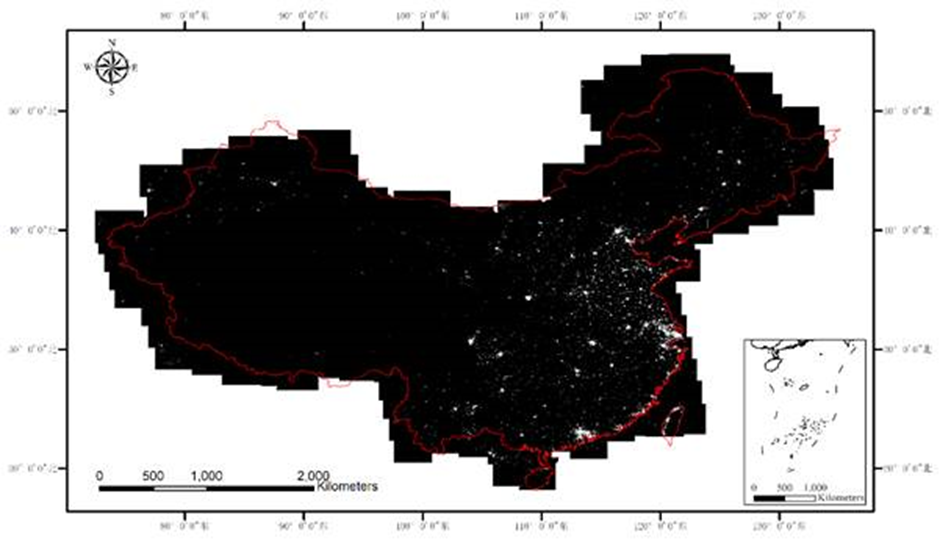
The remotely sensed nighttime light map of China from Luojia-1A 01 satellite
With images captured nationwide by Luojia-1A 01 between June 2018 and December 2018, WHU and High Resolution Earth Observation System Hubei Data and Application Center co-mapped this 250- kilometers wide picture that contains a total of 275 scenes. The drawing is based on ground control points, and it is an orthophoto map with a 130-meter image resolution and a 195-meter geolocation accuracy.
The project team constructs a full-link geometric processing model for images georeferencing through the analysis of the error sources and impact mechanism of Luojia-1A 01. The absolute geolocation accuracy of images is substantially improved by constructing an end-to-end link geometric processing model on air-to-ground positioning and involving ground control points in block adjustment. On this basis, the team uses space-borne imagery to automatically match 1,602 connection points and conducts the block adjustment with control points. After adjustment, the root mean square error of connection points is 0.983 pixels and that of check points is 1.5 pixels. Absolute geolocation accuracy has been increased from the original uncontrolled 683.386 meters to 195.491 meters.
Being the first to combine remote sensing and navigation in the world, Luojia-1A 01, a low-orbit micro-nano scientific experiment satellite, was developed by WHU since 2015 and launched on June 2nd, 2018. Its nighttime light remote-sensing resolution (130 meters, can clearly identify roads and streets) has preceded those of Defense Meteorological satellites (OLS sensor, 2.7 kilometers) and National Polar-orbiting Partnership satellites (VIIRS Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer, 740 meters), which facilitates the conversion from surface monitoring to socioeconomic development monitoring. The feasibility that low-orbit satellites can enhance the signal intensity of COMPASS is brought up and verified for the first time in the world, which will serve the going-global strategy of Beidou-3. So far nighttime light remote-sensing data have been provided for more than 3,000 users in 16 countries and regions, including the United Nations.
Nighttime light images not only reflect urban lights at night, but also capture the movement of fishing boats, natural gas combustion, and the outburst of forest fire and so on. Therefore, it is widely used in fields of socioeconomic parametric estimation, regional development research, major accidents estimation, fishery monitoring and so forth.
The map is released by High Resolution Earth Observation System Hubei Data and Application Center. Access provides upon application. For details please visit website at www.hbeos.org.cn
Rewritten by Zhang Yuting
Edited by Shen Yuxi and Hu Sijia