With athletes breaking Olympic records one after another, the National Speed Skating Oval of the Beijing Winter Olympics, which is affectionately called the “Ice Ribbon”, is worthy of its name as “the fastest ice”. How does the “Ice Ribbon” become a lucky venue for athletes from all over the world? The team of high-definition laser radar led by Professor Mao Qingzhou from Wuhan University played an important role in the construction of “Ice Ribbon”.

Chinese player competing in the “Ice Ribbon” / Xinhua News Agency
“The fastest ice”! “The smoothest ice”!
Mao Qingzhou, professor and doctoral supervisor from the School of Remote Sensing and Information Engineering and the School of Aerospace Science and Technology, Wuhan University, is an expert in the fields of satellite navigation and position and high-definition laser measurement. Why are experts in remote sensing needed in the construction of the National Speed Skating Oval? According to Mao, the major work of his team was the installation of underground ice tubes with high-precision three dimensional laser scanning.

Mao at the construction site of the “Ice Ribbon”
“To meet the goal of ‘the fastest ice’, ice tubes must be paved in the smoothest way,” Mao explained, adding that among the ice rink and the ice tube layer which was of fundamental importance placed a concrete overlay. If the difference between the heights of ice tubes was too large or they were arranged unevenly, the cooling capacity of these tubes would be different once there placed a concrete overlay, which would finally result in different temperatures and thicknesses in different ice surfaces.

Three dimensional lasers are scanning
Covering an area of 12,000 square meters, the ice rink in the National Speed Skating Oval requires an ice tube every 10 centimetres. The work of Mao’s team was to scan and measure the ice rink with high-precision three dimensional laser to form field point cloud data with a precision of at least 2 millimetres so that they could analyse the altitudes and parallelism of ices tubes and identify tubes that needed to be improved.

Neatly-arranged ice tubes
Finally, with the efforts of Mao’s team and construction crew, the project of “Ice Ribbon” achieved an allowable elevation deviation of ±5mm, the parallelism between tubes better than 1/1000, and the largest difference of 0.5℃ of ice surface.

Based on this technology, the project of “Key technology of dynamic high-precision construction measurement in National Speed Skating Oval and its application” co-applied by Wuhan University, Beijing Urban Construction Group Co., Ltd and Shenzhen University won the first prize of Surveying and Mapping Science and Technology Award in 2021.

Mao said, “In the complicated and demanding process of making ice for competition venues for the Beijing 2022 Winter Olympics, our work is just a fundamental one. Many other teams have made great efforts and applied the latest cutting-edge technologies.”
The high-definition laser measurement technology has been widely applied in the subway and high-speed railway projects. It has been used to the routine testing of 80% of Wuhan metro lines and nearly all the high-speed railways in Hubei province to make sure that even a trivial track deviation can be discovered in time.

However, applying this already mature technology to the building of Olympic venues posed new challenges to Mao’s team. According to Mao, “Different from the linear lines measured before, ice tubes that to be measured are area-oriented, which means instead of just measuring the two ends of the tube, we need to measure all the fronts, doubling the calculation. Therefore, we upgraded and improved measuring techniques and mathematical calculation models.

From application in subway and high-speed railway to the “Ice Ribbon”, from being used underground to under-ice, this mature technology has demonstrated its promising future to the world.

From Xinhua News Agency by Zhang Chenlin
“Witnessing the new Olympic records one after another created in the ‘Ice Ribbon’, we, as the participators of the construction, feel pleasant and gratified that our work has been paid off,” said Mao, adding that he was following the Beijing 2022 Winter Olympics and that the goods results achieved by athletes to some extent implied their success in building the “fastest ice” proposed by the venue builder.
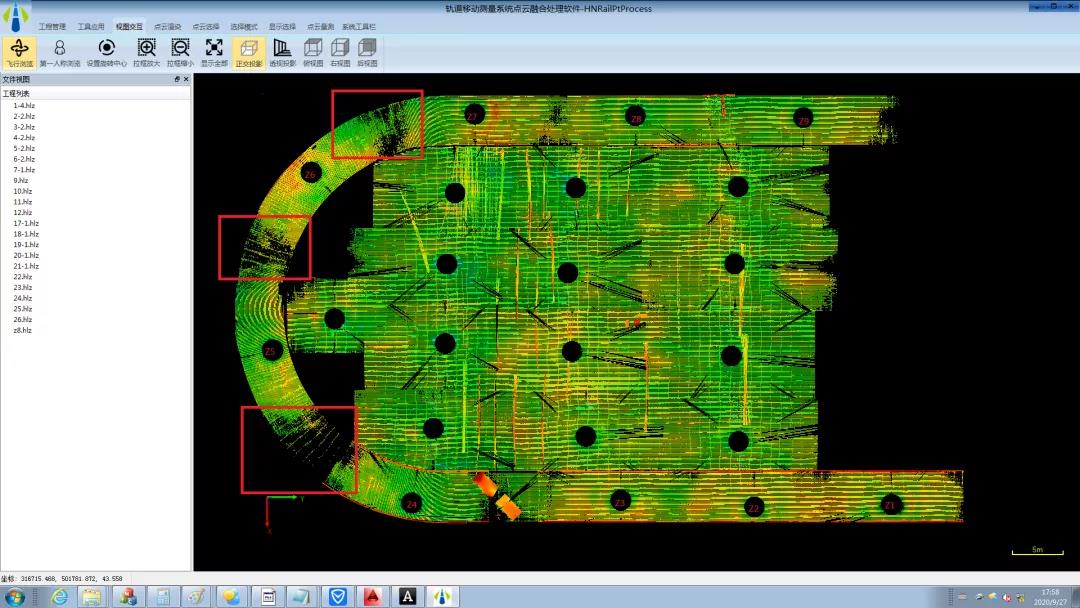

The complete cloud point figure of the ice-manufacture pipe in National Speed Skating Oval
10 people played security roles in the Olympics in Mao’s group and the fall of 2020 they made a comprehensive measurement to the ice-manufacture pipe. After 28 days of data collecting and analyzing, they obtained 2TB of scene point cloud data.
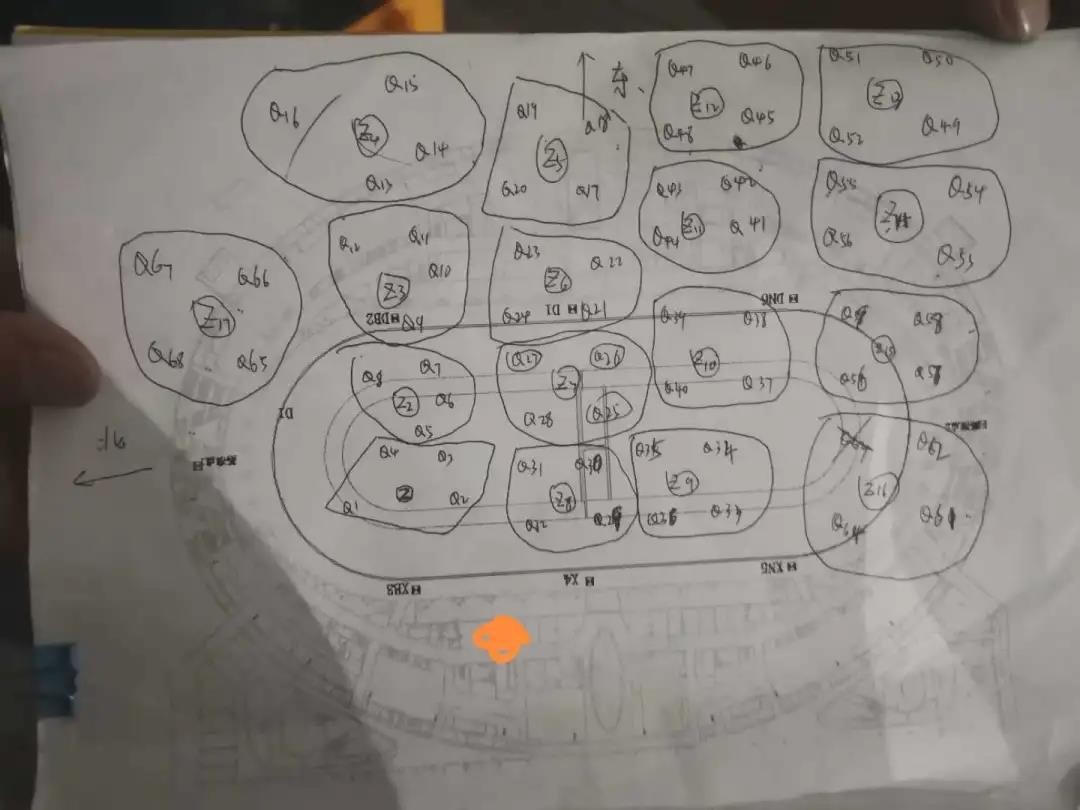
The distribution of the measure stations
“This mission is short in time circle, heavy in engineering tasks and strict in precision. We threw ourselves into this mission, especially the days before the acceptance check. Our data analysis group in Wuhan worked overtime through the night.” said Mao.
What is LIDAR?
The LIDAR group led by Professor Mao provides a safeguard to the construction of “The fastest ice”. So what is LIDAR? How do we apply LIDAR to our daily life?

LIDAR is to expand two dimensional visual figures to three dimensional scene perceptions. Compared with the traditional two-dimensional figures, LISAR has direct access to three dimensional scene information, which means it has the characteristics of initiative, high reliability, high accuracy, high resolution and large FOV.
LIDAR is widely applied in the fields of forest inventory, agricultural forecast, power line maintenance, large venue safety monitoring and coast monitoring and measurement, which act as a backstop of our production.
These years almost every autonomous vehicle and unmanned system are using LIDAR as a vision sensor. The latest applications like BIM, CIM, Digital Twins and Metaverse can no more digitalize three dimensional real world data without LIDAR.
In a certain sense, LIDAR, a technology developed in the last two decades, is in a stage of high development. With the simultaneous development of hardware technology and point cloud intelligent processing, it will have a broader prospect and intelligence requirement in every national economy industry, especially the digital economy. “We need more youths of thought to join.” Mao appeals.
Faster, higher, stronger - together
Valiant athletes are trying to do better
“The fastest ice” together with the fastest speed
There are more records for us to break
Let’s witness in Ice Ribbon
The stars are sparkling at this moment.
Rewritten by Wang Ziyan& Shen Le
Edited by Yin Xiaoxue, Zou Xiaohan and Hu Sijia