Recently, Autophagy, an international journal of cell science, published a paper about autophagy by Prof. Zhou Rongjia and Prof. Cheng Hanhua’s Laboratory of College of Life Sciences.
The paper is titled Gene essentiality of Tubgcp4: dosage effect and autophagy regulation in retinal photoreceptors. (Autophagy, 2019, 15:10, 1834-1837) Dr. Xu Xu from the College of Life Sciences is the first author, and Dr. Shang Dantong from College of Life Sciences comes the second. Prof. Zhou Rongjia is the contact author. Prof. Cheng Hanhua and chief editor of Autophagy Prof. Daniel Klionsky were also participants in this review. This project is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China and National Major Research and Development Program.
Previous study of this team shows that the essential gene Tubgcp4 takes part in autophagy regulation. Once knocked out an allele, spindles are damaged due to dosage effect, which leads to autophagy and photoreceptor degeneration. (Cell Death and Differentiation 2019,DOI: 10.1038/s41418-019-0371-0) This reveals the role of essential genes in molecular mechanisms of autophagy regulation. The review provides a detailed introduction and analysis of genetic essentiality, autophagy regulation and cellular homeostasis.
Human genome contains a set of genes that is essential to survival, namely the essential genome. Both human genome and mice genome contain around a thousand of essential genes. Mutations of the essential genes can cause early embryonic death. Essential genes exist in a variety of species from animals, plants to microorganism, and they are also the most basic genome needed for synthesizing organism. To find out the link between essential genes and cell death is a core issue in study. With the help of gene knock-out technology, the team analyses dosage effect of allele and draws the conclusion that Tubgcp4 deletion results in embryonic death and haploid dosage takes part in autophagy regulation and photoreceptors cellular homeostasis system. Those findings established the inner link between essential genes and cell death, which make a great breakthrough in cellular homeostasis and essential genes function research.
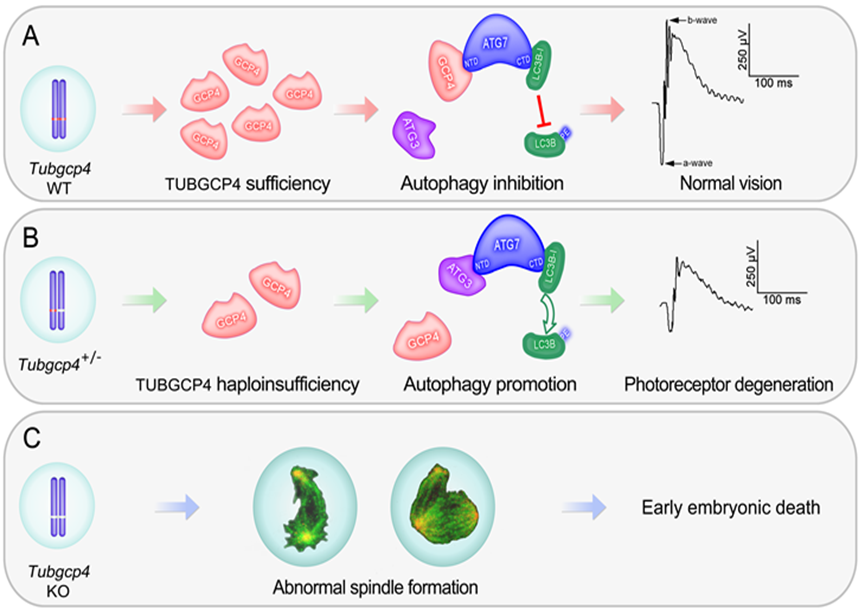
Essential TUBGCP4 gene takes part in early embryonic development and photoreceptor degeneration
Rewritten by Zhang Yuting
Edited by Zhang Shiqi, Shen Yuxi and Hu Sijia