Jie Wei, Xue Gong, Qing Wang, Min Pan, Xiaoqing Liu, Jing Liu, Fan Xia and Fuan Wang*
Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Biology and Medicine (Ministry of Education), College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, P. R. China.
Chem. Sci., 2018, 9, 52–61.
DOI: 10.1039/c7sc03939e
Abstract
|
|
|
|
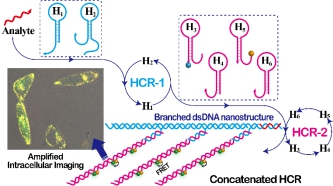
Biomolecular self-assembly has spurred substantial research efforts for the development of low-cost point-of-care diagnostics. Herein, we introduce an isothermal enzyme-free concatenated hybridization chain reaction (C-HCR), in which the output of the upstream hybridization chain reaction (HCR-1) layer acts as an intermediate input to activate the downstream hybridization chain reaction (HCR-2) layer. As a versatile and robust amplification strategy, the unpreceded C-HCR can discriminate DNA analyte from its mutants with high accuracy and specificity. By incorporating an auxiliary sensing module, the integrated C-HCR amplifier was further adapted for highly sensitive and selective detection of microRNA (miRNA), as a result of the hierarchical and sequential hybridization chain reactions, in human serum and even living cells through an easy-to-integrate “plug-and-play” procedure. In addition, the C-HCR amplifier was successfully implemented for intracellular miRNA imaging by acquiring an accurate and precise signal localization inside living cells, which was especially suitable for the ex situ and in situ amplified detection of trace amounts of analyte. The C-HCR amplification provides a comprehensive and smart toolbox for highly sensitive detection of various biomarkers and thus should hold great promise in clinical diagnosis and assessment. The infinite layer of multilayered C-HCR is anticipated to further strengthen the amplification capacity and reliability (anti-invasion performance) of intracellular imaging approach, which is of great significance for its bioanalytical applications.
Full text: http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2018/SC/C7SC03939E#!divAbstract
