The research team led by Professor Tai Qidong from the Institute of Technological Sciences at Wuhan University (WHU) recently published a significant study in Nature Communications.
The paper, titled Spontaneous bifacial capping of perovskite film for efficient and mechanically stable flexible solar cell, reveals a breakthrough in flexible perovskite solar cells (F-PSCs).
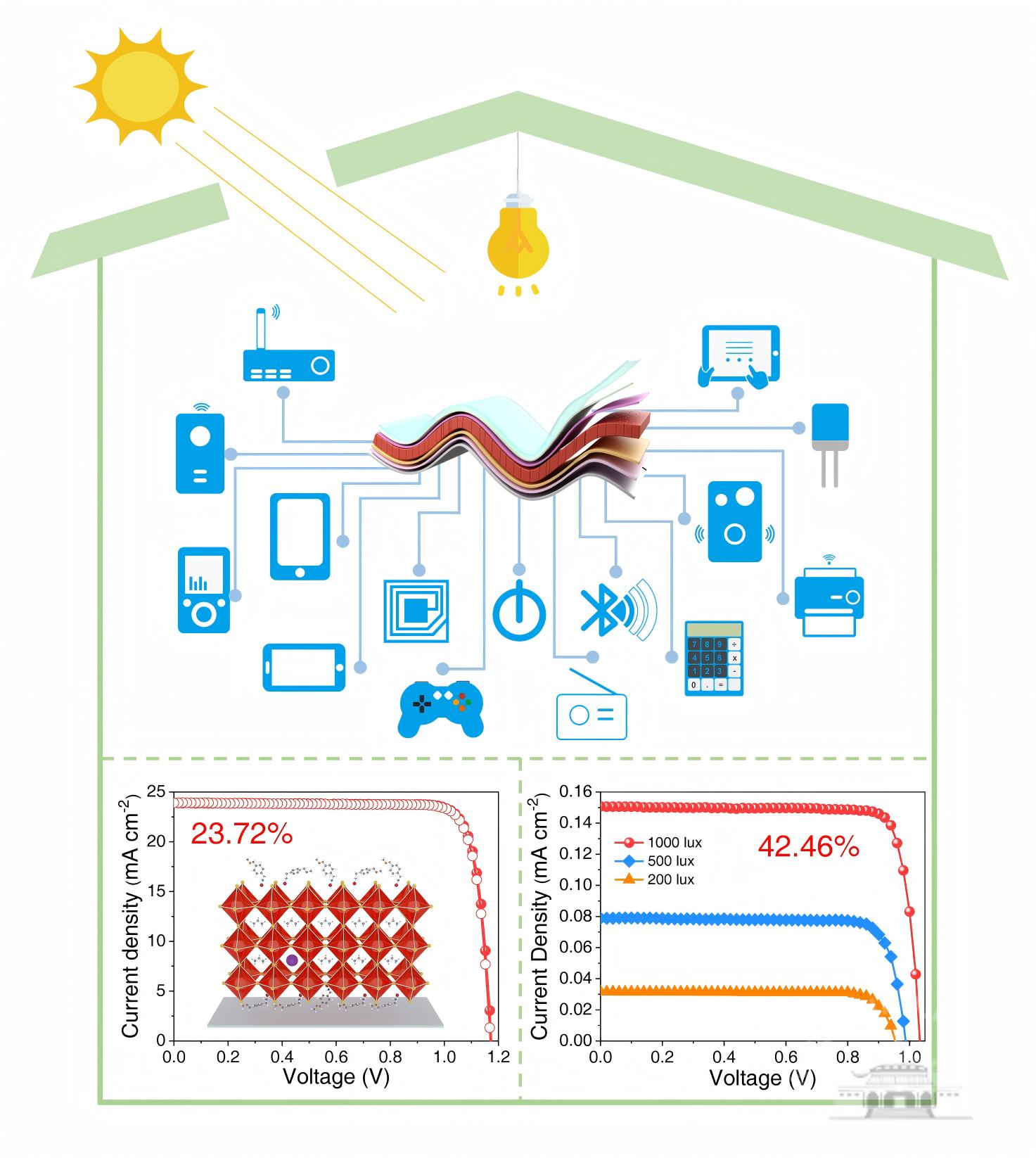
Schematic illustration of various IoT devices powered by indoor PV.
The research team incorporated a precursor additive, 4-methoxybenzylamine hydrobromide (MeOBABr), to achieve spontaneous bifacial capping of perovskite films, which effectively improves the mechanical properties of the grain boundaries.
This method smooths the grain boundary grooves, reducing stress during bending and enhancing the strength and stability of the perovskite film. As a result, the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of the perovskite solar cells is significantly improved.
The study shows that with the addition of MeOBABr, inverted flexible solar cells based on NiOx/PTAA double hole transport layers achieve a PCE of 23.72 percent (certified efficiency 22.9 percent) under AM 1.5G illumination, and a remarkable PCE of 42.46 percent under 1,000-lux indoor lighting, while also demonstrating excellent bending durability.
This research offers new insight into the efficient and stable application of flexible perovskite solar cells, with broad potential for future applications.
Link to paper: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-55652-6