This is a 2 cm long flexible gadget that weighs only 0.3 grams. It can move freely, go up and down steep slopes, carry heavy loads, adapt to all kinds of surfaces and endure extreme temperature.
Recently, Professor Xue Longjian's research group (NISE-Lab) from the School of Power and Mechanical Engineering (WHU) and the Institute of Technological Sciences (WHU) has developed Geca-Robot, an extremely versatile miniature soft robot with precise control of its direction and speed. It is expected to be able to complete a variety of complex operations in the crevices of ruins and the body of organisms.
The paper was recently published on Materials Today, one of the leading journals in the field of materials with an impact factor of 24.372. It was selected as the inside cover article entitled Bioinspired footed soft robot with Unidirectional all-terrain mobility. The first author of the paper is Wang Xin, a doctoral student from the School of Power and Mechanical Engineering (WHU), and the corresponding authors are Professor Liu Sheng and Professor Xue Longjian. The research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.

The paper was selected as inside cover article
Compared with traditional rigid robots, the soft-body robot has more flexibility and deformability. It has great potential in the fields of industrial production and medical rescue, and has received much attention from researchers. However, little attention has been paid to the foot design of mini soft-body robots, and many of them even lack foot design. Without precise foot design, soft-body robots often rely on a rough surface or a specially structured substrate to provide forward movement. The movement process is therefore difficult to control accurately. Moreover, the robot's ability to move on smooth, sloping, or water-filled surfaces may also be limited.
"Our research was inspired by two animals, gecko and caterpillar." Xue Longjian’s team has long worked on biomimetic materials. They found that the unique bristle structure on the gecko's feet could make it move fast and steadily on all kinds of terrain, which can solve the problem of the mini soft robots’ poor adaptability to the moving surface. Therefore, they tried to introduce a gecko-like toe bristle foot to the robot to give it a good surface adaptation.
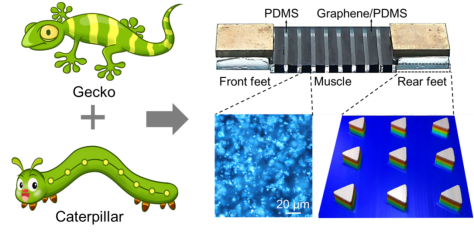
Geca-robot is designed with reference to the adhesive property of gecko feet and the gait of caterpillar
This little gadget has its own feet and muscles. It uses a micro-prism array of imitated gecko bristles as a "foot" and alternating bands of transparent PDMS and graphene / PDMS composites (GP) as "muscles". The gait is based on the gecko foot's adhesion and the caterpillar's alternating motion pattern of forefeet and hindfeet. When exposed to light (from ultraviolet to infrared), its forefeet move forward, and when the light is turned off, its hind feet move forward. Alternating beams of light provide it with driven forces to move forward.
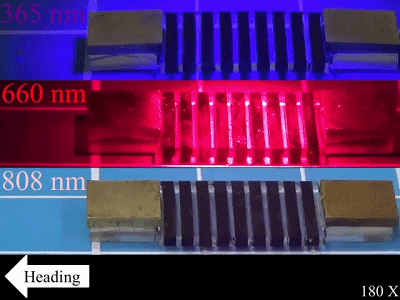
Movement driven by full-wave band light
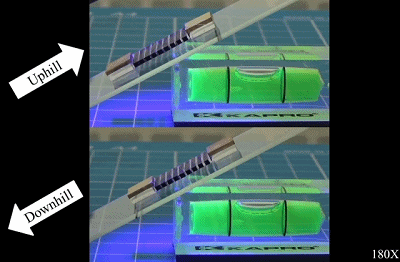
Moving uphill and downhill
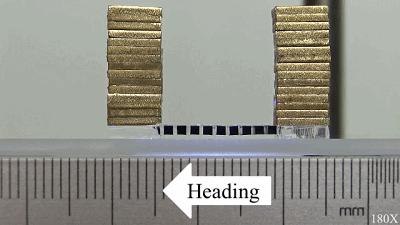
Carrying heavy loads
Despite its small size, the Geca-Robot has remarkable abilities: Its bionic foot structure provides it with the best non-slip running shoes which allow it to move on either rough or smooth surfaces without slipping.
The hydrophobic structure allows it to move on watery surfaces. Even if the water covers its feet, its movement will not be hindered.
Bionic foot design and caterpillar-like gait enable it to anchor and walk steadily on a smooth surface with a slope of up to 30 degrees without slipping.
It can function in temperatures ranging from -20 to 100 degrees and can adapt to extreme temperature changes.
In addition, it is a "Hercules". It can load more than 50 times its own weight under stable movement conditions. Because of its good adaptability to various surfaces and load capability, and its ability to be controlled remotely from ultraviolet to infrared, Geca-Robot is suitable for working in narrow and harsh environments. For example, geological exploration can be carried out in crevices and deep pits, search and rescue, and target location can be carried out in crevices of ruins. Drug delivery or focus detection in biological organs or blood vessels with complex surface topography, acid-base property, temperature and humidity can be achieved with the help of skin-penetrating infrared light source. Therefore, Geca-Robot has great application potential.
Rewritten by Liu Tongxv
Edited by Qin Zichang, Sylvia and Hu Sijia