On September 2, the well-known international academic journal Genome Medicine, (IF=10.675) published online the latest findings on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which resulted from research conducted by Associate Professor Sun Chengcao, Professor Li Dejia and Professor He Qiqiang’s research group from the School of Health Sciences, Wuhan University (WHU).
The article is entitled FOXC1-mediated LINC00301 Facilitates Tumor Progression and Triggers an Immune-suppressing Microenvironment in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer by Regulating the HIF1α Pathway. The three co-first authors are Sun Chengchao, Zhu Wei, a doctoral candidate of the class of 2017 from WHU, and Dr. Li Shujun from the Wuhan Prevention and Treatment Center for Occupational Diseases. The co-corresponding authors are Sun Chengcao, Li Dejia and He Qiqiang. This study was supervised by Professor Liuqing Yang and Professor Chunru Lin from the University of Texas’ M. D. Anderson Cancer Center.
NSCLC is the leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Clarifying the mechanisms that underlie the occurrence and development of NSCLC and improving diagnosis and treatment is of great urgency. In this study, the research group found and reported for the first time a new lncRNA—LINC00301, which was significantly expressed in NSCLC samples and cell lines, and is closely associated with the prognosis of NSCLC patients. This research reveals the oncogenic role of LINC00301 in NSCLC clinical specimens as well as cellular and animal experiments, elaborating the specific effect and the molecular regulation mechanism of LINC00301 in NSCLC tumorigenesis, tumor progression, metastasis and the formation of an immune -suppressive microenvironment, thus providing new insights into the tumorigenesis and immunotherapy of NSCLC. Combined with locked nucleic acid (LNA) FISH technology, LINC00301 has the potential to be used as a diagnostic and therapeutic target for NSCLC.
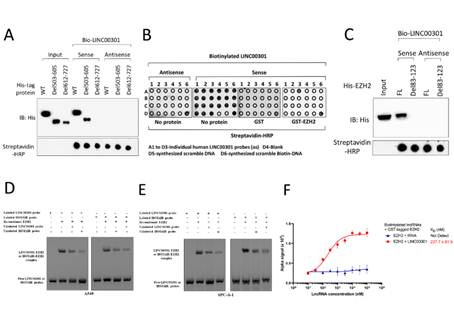
Validating the direct binding sites between LINC00301 with EZH2 protein.
Article Link:https://genomemedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13073-020-00773-y
Written by: Sun Chengchao
Rewritten by: Shi Shang
Edited by:Zhu Tong, Sylvia and Hu Sijia